Apache airflow는 에어비앤비에서 만든 워크플로우 관리 시스템입니다. 본 포스팅에서는 기초적인 airflow DAGs 작성 예시와 사용법을 정리합니다.
Basics
- DAG: Task의 집합
- Task: Airflow DAGs의 기본 실행 단위
- Operator: Task 구현을 위한 템플릿. 제일 기본적으로는 BashOperator와 PythonOperator가 존재하고, 그 외에 SQL Operator, Http Operator 등 존재
- Sensor: 외부 이벤트에 대해 특정 조건 만족하는지 주기적으로 확인
- XComs (i.e., cross-communications): XComs를 통해 task간 정보 주고받을 수 있음. JSON은 지원하지만 dataframe 같은 용량이 큰 데이터는 지원하지 않음. 따라서 데이터 용량이 큰 경우에는 특정 다른 공간에 저장한 뒤 저장된 위치를 XComs로 전달하는게 일반적인 디자인 패턴
- Task Lifecycle:
no_statusScheduler{status}Executor{status}Worker{status}
Installation
로컬 가상환경에서 pip를 통해 airflow를 설치하여 사용하거나, airflow docker 이미지를 pull 받아 사용하는 방법이 존재합니다. 이 중 docker를 활용하는 방식을 권장드립니다.
Airflow w. PIP Install
- 공식 저장소에서 airflow 버전 및 다운 방법을 확인하여 다운 받습니다.
export AIRFLOW_HOME=.환경 변수 설정을 합니다.- Airflow DB, 웹 서버, 스케줄러를 각각 실행합니다:
airflow db init,airflow webserver -p 8080,airflow scheduler airflow users create --help명령어를 통해 유저 설정 방법을 확인하고, username, password를 설정합니다.- localhost:8080/ 에 접속하여 웹서버가 잘 작동하는지 확인합니다.
Airflow w. Docker
- 다음 명령을 통해 compose file을 다운받습니다:
curl -Lf0 'https://airflow.apache.org/docs/apache-airflow/2.0.1/docker-compose.yaml" mkdir ./dags ./logs ./plugins명령을 통해 기본 디렉토리들을 생성합니다.- 초기화 및 compose 파일 실행을 순서대로 진행합니다:
docker-compose up airflow-init,docker-compose up -d - localhost:8080/ 에 접속하여 웹서버가 잘 작동하는지 확인합니다.
- webserver 컨테이너에서
airflow users create --help명령어를 통해 유저를 생성할 수 있습니다. (기본 유저는 name:airflow, passwd: airflow)
DAGs
docker-compose.yaml 파일에서 AIRFLOW__CORE__LOAD_EXAMPLES 옵션을 true로 설정하면 다양한 DAG 예시를 확인하실 수 있습니다.
Example Code: Hello World!
이 곳에서도 간단한 예시 코드를 확인 가능합니다.
start_date: 시작되는 기준 시점. 즉, 실제 실행은 'start_date + 주기'부터 시작execution_date: 실제 실행 날짜가 아닌 예약을 시도한 시간 (historical name for what is called a logical date)catchup: current date과 start date에 차이가 있어 과거 데이터에 대해서도 DAG가 실행 되어야하는 경우 활용. False로 지정시에는 최근 DAG만 실행backfill: 스케줄 시점이 지나간 DAG 실행할 때 활용retries: task가 실패했을 때 재실행을 시도retry_delay: 재시도 전에 wait할 시간
from datetime import datetime
from airflow import DAG
from airflow.operators.bash import BashOperator
default_args = {
'owner': 'yuhodots',
'retries': 5,
'retry_delay': timedelta(minutes=2)
}
with DAG(
dag_id='first_dag',
default_args=default_args,
description='first dag'
start_date=datetime(2023, 9, 1, 2),
schedule_interval='@daily'
) as dag:
task1 = BashOperator(
task_id='first_task',
bash_command="echo hello world, this is the first task!"
)
task2 = BashOperator(
task_id='second_task',
bash_command="echo hello world, this is the second task!"
)
task1 >> task2 # same with `task1.set_downstream(task2)`from datetime import datetime
from airflow import DAG
from airflow.operators.python import PythonOperator
default_args = {
'owner': 'yuhodots',
'retries': 5,
'retry_delay': timedelta(minutes=2)
}
def greet(name, age):
print(f"Hello world! My name is {name} and {age} years old")
with DAG(
dag_id='first_dag',
default_args=default_args,
description='first dag'
start_date=datetime(2023, 9, 1, 2),
schedule_interval='@daily'
) as dag:
task1 = PythonOperator(
task_id='first_task',
python_callable=greet,
op_kwargs={'name': 'Yuho Jeong', 'age': 27}
)
task1with DAG (...) as dag: 대신에 아래와 같은 형태도 가능합니다.
from airflow.decorators import dag
from airflow.operators.python import PythonOperator
def greet(name, age):
print(f"Hello world! My name is {name} and {age} years old")
@dag(...)
def greet_dag():
task1 = PythonOperator(
task_id='first_task',
python_callable=greet,
op_kwargs={'name': 'Yuho Jeong', 'age': 27}
)
task1
dag = greet_dag()XComs
XComs를 통해 task간 정보를 주고받는 것은 TaskInstance 객체의 xcom_push, xcom_pull 메소드를 통해 가능합니다.
from airflow.decorators import dag
from airflow.operators.python import PythonOperator
from airflow.models import TaskInstance
def test_xcoms_push(ti: TaskInstance):
ti.xcom_push(key="first_item", value=['first_item'])
ti.xcom_push(key="second_item", value=['second_item'])
def test_xcoms_pull(ti: TaskInstance):
item1 = ti.xcom_pull(key="first_item", task_ids="test_xcoms_push")
item2 = ti.xcom_pull(key="second_item", task_ids="test_xcoms_push")
print(item1, itme2)
@dag(...)
def dag_function():
task1 = PythonOperator(
task_id='test_xcoms_push',
python_callable=test_xcoms_push,
)
task2 = PythonOperator(
task_id='test_xcoms_pull',
python_callable=test_xcoms_pull,
)
task1 >> task2
dag = dag_function()Connection
Webserver의 Admin 탭에서 connection 설정을 할 수 있습니다. Connection은 외부 연결을 관리해주며, 일반적으로 클라우드에 존재하는 DB 서버, Datalake 등의 연결을 목적으로 활용됩니다.
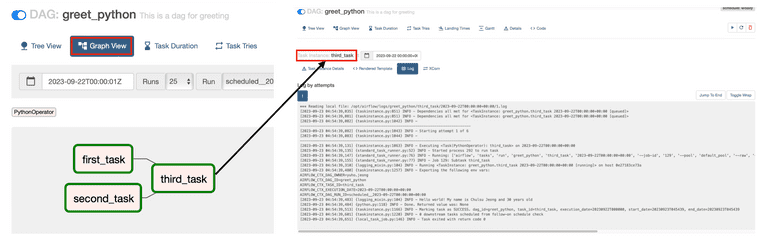
Graph View & Log
DAG 구조를 graph view를 통해 한 눈에 확인이 가능하고, 각 노드의 실행 결과는 각 노드를 클릭하면 나오는 log 내에서 확인이 가능합니다.
Debugging
DAG 스크립트 파일의 가장 아래에 해당 코드를 추가해줍시다. 그러면 vscode 같은 IDE에서 디버깅이 가능합니다! (with .vscode/launch.json)
# with DAG(...) as dag:
if __name__ == "__main__":
dag.test()Re-run
- Catchup은 DAG 배포가 start_date 설정 보다 더 나중일 때, 과거의 배치작업을 수행해줌. 이 외에 backfill 혹은 clear를 통해 이전에 돌았던 배치작업을 재수행 해줄 수 있음
- Backfill command:
airflow dags backfill -s <START_DATE> -e <END_DATE> <DAG_ID> - Clear: airflow web UI 상에서 원하는 배치작업을 clear
References
아래의 자료들을 같이 참고하면 좋습니다.
- Apache Airflow DAGs: https://airflow.apache.org/docs/apache-airflow/stable/core-concepts/dags.html
- Airflow Tutorial for Beginners - Full Course in 2 Hours 2022: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=K9AnJ9_ZAXE&t=37s
- Google Gloud DAG documents: https://cloud.google.com/composer/docs/how-to/using/writing-dags?hl=ko