Deep learning 기반의 object detection 알고리즘에 대해 리뷰합니다. Two-stage detector와 one-stage detector 알고리즘 중에서 유명한 알고리즘들을 위주로 간단히 정리하였습니다. 오타나 정확하지 않은 내용에 대해서 댓글 달아주시면 감사합니다.
Introduction
- Localization: Object의 위치를 bouding box 형태로 알아내는 task
- Object detection: 이미지 내에 다수의 object가 존재할 때, 각각의 class를 맞추고 localization 하는 task
- RoI: Region of Interest
- Region proposal: Object가 있을 것 같은 영역을 제안
- Selective search (e.g., Fast R-CNN): 인접한 region 사이의 유사도를 측정하고, 점점 큰 영역으로 통합하는 방법
- Sliding window, Spatial anchor, RPN (e.g., Faster R-CNN): 다양한 크기의 window를 이미지 상에서 sliding 하면서 해당 위치에 물체가 존재하는지 확인하는 방법. 해당 유튜브 영상에서 정말 잘 설명해주고 있음
- Localization layer: Bbox position를 제안하는 layer이고 일반적으로 regressor 활용
- Classification layer: Object의 class를 제안하는 layer
- RoI Pooling: RPN을 통해 나온 Proposal의 크기가 다 다른데, RoI pooling을 거치면 모두 사이즈가 같아짐 (e.g., Output size = 7x7 pooled feature)
- RoIAlign: mask R-CNN (Instance Segmentation model)에서 사용. RoI Pooling과 output size는 동일한데 pooling 값 계산하는 방식이 다름. 이후 연구들은 대부분 RoIAlign 사용함
- IoU (Intersection of Union): 예측 bbox와 정답 bbox가 겹치는 비율
# Code by ChatGPT
def compute_iou(box, boxes):
"""
Computes the IOU between a given box and a set of boxes.
:param box: Numpy array with shape (4,) representing the coordinates of a bounding box.
:param boxes: Numpy array with shape (N, 4) representing the coordinates of N bounding boxes.
:return: Numpy array with shape (N,) containing the IOUs between the box and the N bounding boxes.
"""
# Calculate coordinates of intersection boxes
x1 = np.maximum(box[0], boxes[:, 0])
y1 = np.maximum(box[1], boxes[:, 1])
x2 = np.minimum(box[2], boxes[:, 2])
y2 = np.minimum(box[3], boxes[:, 3])
# Calculate area of intersection boxes and union boxes
intersection = np.maximum(0.0, x2 - x1) * np.maximum(0.0, y2 - y1)
area_box = (box[2] - box[0]) * (box[3] - box[1])
area_boxes = (boxes[:, 2] - boxes[:, 0]) * (boxes[:, 3] - boxes[:, 1])
union = area_box + area_boxes - intersection
# Calculate IOU and return
iou = intersection / union
return iou- Non-Maximum Suppression (NMS): 여러 개의 bbox가 동일한 class로 분류되면서 겹치는 경우에는 하나로(혹은 일부로) bbox 예측을 줄이는 방법
# Code by ChatGPT
def non_maximum_suppression(bounding_boxes, confidence_scores, overlap_threshold):
"""
Implements Non-Maximum Suppression on a set of bounding boxes and corresponding confidence scores.
:param bounding_boxes: Numpy array with shape (N, 4) representing the coordinates of the N bounding boxes.
:param confidence_scores: Numpy array with shape (N,) representing the confidence scores for the N bounding boxes.
:param overlap_threshold: Float representing the maximum allowed overlap between two bounding boxes.
:return: List with the indices of the selected bounding boxes.
"""
# Sort bounding boxes by their confidence scores (highest to lowest)
sorted_indices = np.argsort(-confidence_scores)
selected_indices = []
while sorted_indices.size > 0:
# Select bounding box with highest confidence score
best_box_index = sorted_indices[0]
selected_indices.append(best_box_index)
# Compute the IOUs between the selected bounding box and the remaining boxes
remaining_indices = sorted_indices[1:]
overlaps = compute_iou(bounding_boxes[best_box_index], bounding_boxes[remaining_indices])
# Discard boxes with IOU greater than overlap threshold
non_overlapping_indices = np.where(overlaps <= overlap_threshold)[0]
sorted_indices = remaining_indices[non_overlapping_indices]
return selected_indicesEvaluation Metric
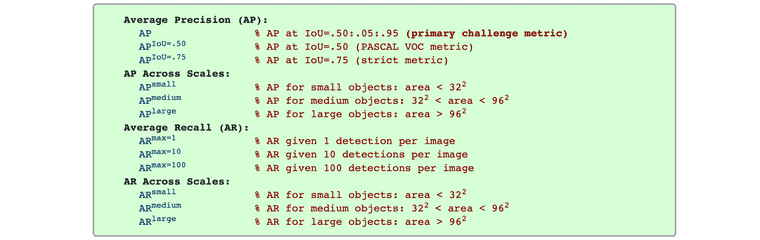
- Average Precision (AP .5): IoU 0.5 이상을 true positive로 인식
- 11점 보간법과 모든점 보간법 계산법
-
AP[.5:.05:.95]: AP .5, AP .55, ..., AP .95의 값을 모두 측정하여 평균. 모든점 보간법을 이용해서 AP를 구한 값의 평균, 즉, Precision-Recall Curve의 아래 면적을 의미
-
mean Average Precision: 기본적으로 precision은 하나의 object에 대한 검출을 의미하므로, mAP는 각각의 class에 대해 AP[.5:.05:.95]를 계산하고 평균을 산출했다는 의미
Taken from https://cocodataset.org/#detection-eval
- Macro: '평균의 평균'을 구하는 방법. macro precision = (precision 1 + precision 2 + ... + precision K) / K where K is the number of classes
- Micro: '전체의 평균'을 구하는 방법. micro precision = TP / (TP + FP)
Two-Stage Detector
Region proposals을 먼저 생성 한 이후에 object classification and bbox regression 수행. 따라서 속도가 느리지만 일반적으로 성능이 좋음 (최근에는 꼭 그렇지도 않은듯)
Taken from Wu, Xiongwei, Doyen Sahoo, and Steven CH Hoi.
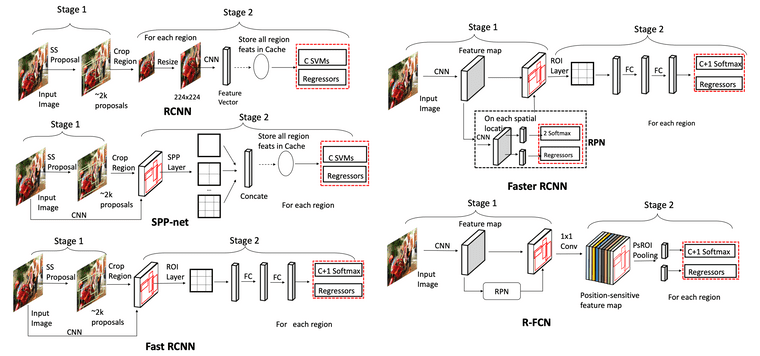
R-CNN (2014)1
Region-Based Convolutional Neural Networks
- 이미지에 대해 selective search를 이용하여 약 2000개의 RoI 추출. Selective search에 대한 설명은 이곳 참고
- 각 RoI들을 warping (i.e., transforming image regions to a fixed size)
- Warped image에 대해 CNN으로 feature 추출
- Feature를 활용하여, SVM으로는 classification, regressor로는 bbox 예측(i.e., {x, y, width, height})을 수행
Fast R-CNN (2015)2
- 이미지에 대해 selective search를 이용하여 약 2000개의 RoI 추출 (R-CNN과 동일)
- 입력 이미지를 그대로 CNN에 넣어 feature map을 추출. 즉, 입력 이미지가 CNN에 한 번만 forwarding 되어도 됨
- RoI projection: 각각의 RoI를 feature map dimension으로 projection
- RoI pooling 수행: Feature map에서의 각 RoI 영역에 대해 max-pooling 적용해서 NxN matrix 추출
- 최종 feature를 활용하여 softmax layer으로는 classification, regressor로는 bbox 예측을 수행
Faster R-CNN (2015)3
Prior works의 region proposal 방식이 bottleneck이었는데, RPN을 통해 end-to-end 형태의 구조 제안하여 성능 향상
- 이미지를 CNN에 넣어 feature map을 추출
- Feature map을 region proposal network(RPN)으로 보내 feature map에 대한 RoI 생성
- RPN은 기본적으로 여러 개의 서로 다른 형태의 anchor boxes를 사용한 sliding window 방식 사용
- RPN의 final layer에는 물체가 있는지 없는지 판단하는 2-softmax와, bbox 제안하는 regressor가 존재
- 2-softmax와 regressor ouput을 기반으로 RoI 생성하고 이를 RoI pooling layer로 전달
- RoI pooling 수행
- 최종 feature를 활용하여 softmax layer으로는 classification, regressor로는 bbox 예측을 수행
Recap.
| Conference | Region proposal | Classification layer | Localization layer | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| R-CNN | CVPR 2014 | Selective search (CPU) | SVMs | Regressor |
| Fast R-CNN | ICCV 2015 | Selective search (CPU) | Softmax | Regressor |
| Faster R-CNN | NeurIPS 2015 | Sliding window w. RPN (GPU) | Softmax | Regressor |
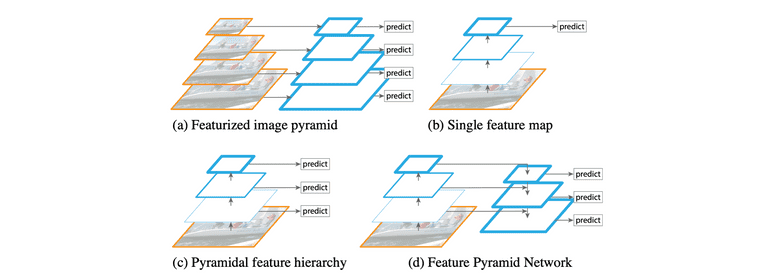
Feature Pyramid Networks (2017)4
Multi-resolution 정보를 최대한 활용하여 object detection 성능 향상을 이루고자 하는 연구들 많았는데 FPN도 그 중 하나임. 다양한 object detection 모델들의 backbone으로 활용되어 성능을 높여줌
- Featurized image pyramid: 입력 이미지를 여러 크기로 resize 하여 각각 CNN에 통과시켜 feature map 획득하는 방법. 당연히도 매우 느림
- Single feature map: 가장 마지막 feature map만 예측에 활용하므로 작은 object에 대한 정보 잘 잡지 못할 것임
- Feature Pyramid Network (FPN)
- Bottom-up pathway와 top-down pathway 형태로 구성됨
- Top-down pathway에서는 이전 layer feature와 bottom-up feature를 입력으로 받아 (adding 후에) upsampling 수행하여 feature map 뽑아내는데, 매 top-down pathway 마다의 feature map를 RPN(region proposal network)에 넣어 모델 예측 출력 가능
- 즉, FPN 사용하면 multi-resolution feature를 뽑아내어 더 나은 object detection 가능
Taken from Tsung-Yi Lin, et al.
# Sample code from https://github.com/jwyang/fpn.pytorch/blob/master/lib/model/fpn/fpn.py#L159
...
def forward(self, im_data, im_info, gt_boxes, num_boxes):
batch_size = im_data.size(0)
im_info = im_info.data
gt_boxes = gt_boxes.data
num_boxes = num_boxes.data
# Bottom-up
c1 = self.RCNN_layer0(im_data)
c2 = self.RCNN_layer1(c1)
c3 = self.RCNN_layer2(c2)
c4 = self.RCNN_layer3(c3)
c5 = self.RCNN_layer4(c4)
# Top-down
p5 = self.RCNN_toplayer(c5)
p4 = self._upsample_add(p5, self.RCNN_latlayer1(c4))
p4 = self.RCNN_smooth1(p4)
p3 = self._upsample_add(p4, self.RCNN_latlayer2(c3))
p3 = self.RCNN_smooth2(p3)
p2 = self._upsample_add(p3, self.RCNN_latlayer3(c2))
p2 = self.RCNN_smooth3(p2)
p6 = self.maxpool2d(p5)
rpn_feature_maps = [p2, p3, p4, p5, p6]
mrcnn_feature_maps = [p2, p3, p4, p5]
rois, rpn_loss_cls, rpn_loss_bbox = self.RCNN_rpn(rpn_feature_maps, im_info, gt_boxes, num_boxes)One-Stage Detector
Pre-generated region proposals 없이 object classification and bbox regression 수행
Taken from Wu, Xiongwei, Doyen Sahoo, and Steven CH Hoi.
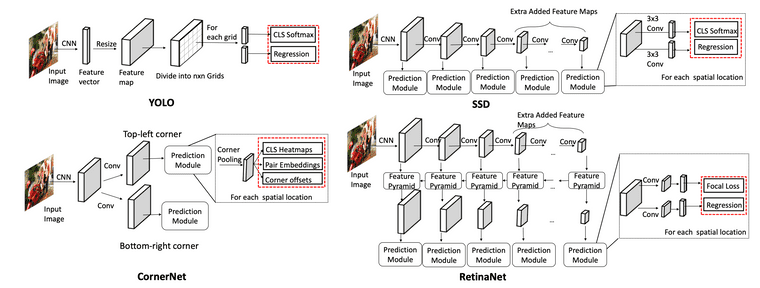
YOLO (2016)5
- 이미지를 N x N grid로 분할 (N=7)
- 이미지를 CNN에 넣고 feature vector를 뽑아냄
- 해당 feature vector를 resize해서 N x N x D의 feature map으로 변형
- N x N이 각각의 grid를 의미하는데, 하나의 D size feature를 (x, y, w, h, confidence socre)과 (class probabilities)로 활용
# Sample code from https://github.com/motokimura/yolo_v1_pytorch/blob/master/yolo_v1.py
...
def forward(self, x):
S, B, C = self.feature_size, self.num_bboxes, self.num_classes
x = self.features(x)
x = self.conv_layers(x)
x = self.fc_layers(x)
x = x.view(-1, S, S, 5 * B + C)
return xRetinaNet (2017)7
- Backbone으로 FPN 사용함
- Foreground, background의 imabalance를 해결하기 위한 focal loss 제안. Easy negative example보다 hard example에 더 많은 가중치를 주는 효과 가짐
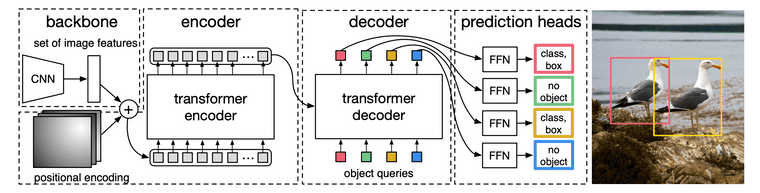
DETR (2020)8
- Prior works들이 NMS나 spatial anchors(RPN) 같은 hand-designed components 너무 많이 요구함. 따라서 customized layer drop하는 단순한 구조 제안
- Bipartite matching (e.g., Hungarian algorithm): 기존엔 set prediction problem을 NMS 등으로 간접적으로 해결했는데, bipartite matching은 object 출력을 아예 N개로 고정시켜 버려서 directly predicts the set of detections
- 예를 들어 N=10이고 object=2라면, 8개는 no object로 예측하면 됨
Taken from Nicolas Carion, et al.
- CNN 활용하여 image feature 추출. Image feature는 의 shape의 feature map인데, 이고, 이미지의 height , width 라 할 때 임
- Image feature map에 positional encoding 더하여 transformer encoder에 입력
- Decoder에 object queries와 encoder output을 입력. 이 때, object query는 N개(max obejct 수)임
- Decoder output을 각각 feed forward network에 입력하고, object가 있는지 없는지, 있다면 class는 무엇이고 bbox는 어떻게 되는지를 출력
- 최종 (prediction head의) 출력에 대해 bipartite matching (i.e., Hungarian algorithm) 수행 후, loss 계산하여 모델 학습. Class prediction loss와 Generalized IoU 활용한 box loss 사용
Quick Overview
- YOLO: 실시간 객체 탐지를 위해 개발된 모델로, 이미지 전체를 한 번에 처리하여 객체를 감지하는 방식. 전통적인 슬라이딩 윈도우 방식과 달리, 이미지 전체를 단일 네트워크로 처리하여 속도가 매우 빠름. 입력 이미지를 SxS 그리드로 나누고, 각 그리드 feature마다 (x, y, w, h, confidence socre)과 (class probabilities) 출력
- YOLOX: YOLO 모델에 Anchor free 방법을 적용해서 성능을 향상. 이외에도 다양한 기술 적용 (Decoupled head , SimOTA, multi-positives, etc)
- Anchor free: 각 그리그마다 3개씩 예측하던 것을 1개로 변경하고 직접 4개의 값을 예측(left-top corner, height, width). FCOS 방식을 생각하면 쉬움
- RCNN(Region-based Convolutional Neural Network): 객체 탐지를 위해 제안된 최초의 Region Proposal 기반 방법 중 하나. 입력 이미지에서 여러 개의 Region Proposal을 생성한 후, 각 Region Proposal에 대해 CNN을 적용하여 피쳐를 추출하고, 이를 기반으로 객체 클래스와 위치를 예측
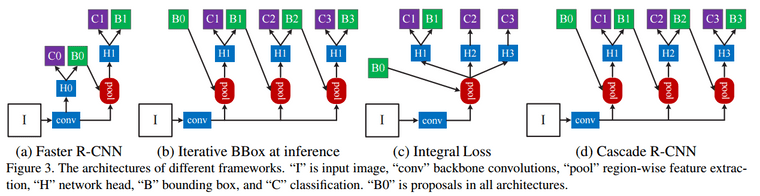
- Cascade RCNN: 여러 단계의 검출기(Detector)를 사용하여 탐지의 정확성을 점진적으로 향상시키는 방법. 각 단계에서는 이전 단계에서 검출된 객체를 기반으로 더 세밀한 검출을 수행. (1) 0.5 IoU로 학습한 detector로 region proposal을 생성하고, (2) 생성된 region proposal로 0.6 IoU인 detector을 학습하고, (3) 0.7 IoU detector도 같은 방식으로 학습. (4) 3-stage가 실험적으로 적합했다고 하며, inference 시에도 cascade 방식으로 수행. 객체 크기가 다양하거나 경계 상자 예측이 어려운 상황에서 특히 효과적이라고 함
- DETR: DETR은 객체 탐지에 Transformer 구조를 도입한 모델. 먼저 CNN backbone으로 C(2048)×H×W image feature를 추출. 이후, 1x1 conv 사용하여 C=256으로 차원을 줄여서 256 dimension의 H×W tokens를 만들어 냄. 이를 encoder에 한번 넣고, encoder 출력과 object query를 decoder에서 cross attention 수행. 최종 object query ouput을 예측에 사용. Region Proposal과 같은 추가적인 단계 없이도 정확한 탐지를 수행할 수 있으며 end-to-end 학습이 가능.
- DN-DETR: 훈련 초기의 모호한 이분 매칭이 느린 수렴으로 이어져, 노이즈를 섞은 GT 박스에 대해 노이즈 제거를 통해 훈련 가속화
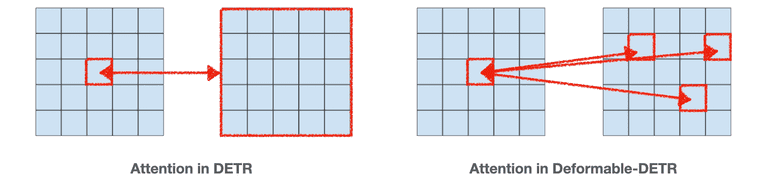
- Deformable-DETR: Deformable Attention Mechanism 도입. DETR보다 빠른 수렴 속도를 가지며 작은 객체에 대한 탐지 성능도 개선
- DINO (DETR with Improved Noise optimization): Contrastive DeNoising Training 도입. N개의 GT box에 대해 양성과 음성 쿼리를 생성하여 총 2N개의 쿼리 생성. 같은 GT 박스에 대해 positive 샘플에는 적은 노이즈 λ1을, negative 샘플에는 큰 노이즈 λ2를 추가. Negative에 대해 no object 예측을 하도록 훈련. DETR 계열 모델 중에서도 최상위 성능
- BoxInst: Weakly-supervised instance segmentation 방법. Projection loss term (모델의 mask예측의 x, y축 방향 projection과, box GT가 얼마나 비슷한지를 측정)과 pairwise loss term (두 pixel 사이의 색상이 유사하면 이 둘이 같은 label을 가지는 경우가 많다고 주장하며, 가까운 pixel에 대해서 유사한 색상을 가지면 같은 객체로 예측되도록 유도) 제안
References
Blog Posts
- https://lilianweng.github.io/posts/2017-12-31-object-recognition-part-3/
- https://lilianweng.github.io/posts/2018-12-27-object-recognition-part-4/
Papers
- Girshick, Ross, et al. "Rich feature hierarchies for accurate object detection and semantic segmentation." Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition. 2014.↩
- Girshick, Ross. "Fast r-cnn." Proceedings of the IEEE international conference on computer vision. 2015.↩
- Ren, Shaoqing, et al. "Faster r-cnn: Towards real-time object detection with region proposal networks." Advances in neural information processing systems 28 (2015).↩
- Lin, Tsung-Yi, et al. "Feature pyramid networks for object detection." Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition. 2017.↩
- Redmon, Joseph, et al. "You only look once: Unified, real-time object detection." Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition. 2016.↩
- Lin, Tsung-Yi, et al. "Focal loss for dense object detection." Proceedings of the IEEE international conference on computer vision. 2017.↩
- Carion, Nicolas, et al. "End-to-end object detection with transformers." Computer Vision–ECCV 2020: 16th European Conference, Glasgow, UK, August 23–28, 2020, Proceedings, Part I 16. Springer International Publishing, 2020.↩